
The 2023 acquisition of VMware by Broadcom significantly affected the world of enterprise software and cloud computing.
Because there are so many unknowns—whether the cost of VMware will rise, what type of support the product will offer, and its future compatibility with other applications—many business owners are scrambling to look for the best VMware alternatives.
In this article, we’re looking at three main competitors to VMware: Hyper-V, Nutanix, Proxmox.
Hyper-V vs. VMware
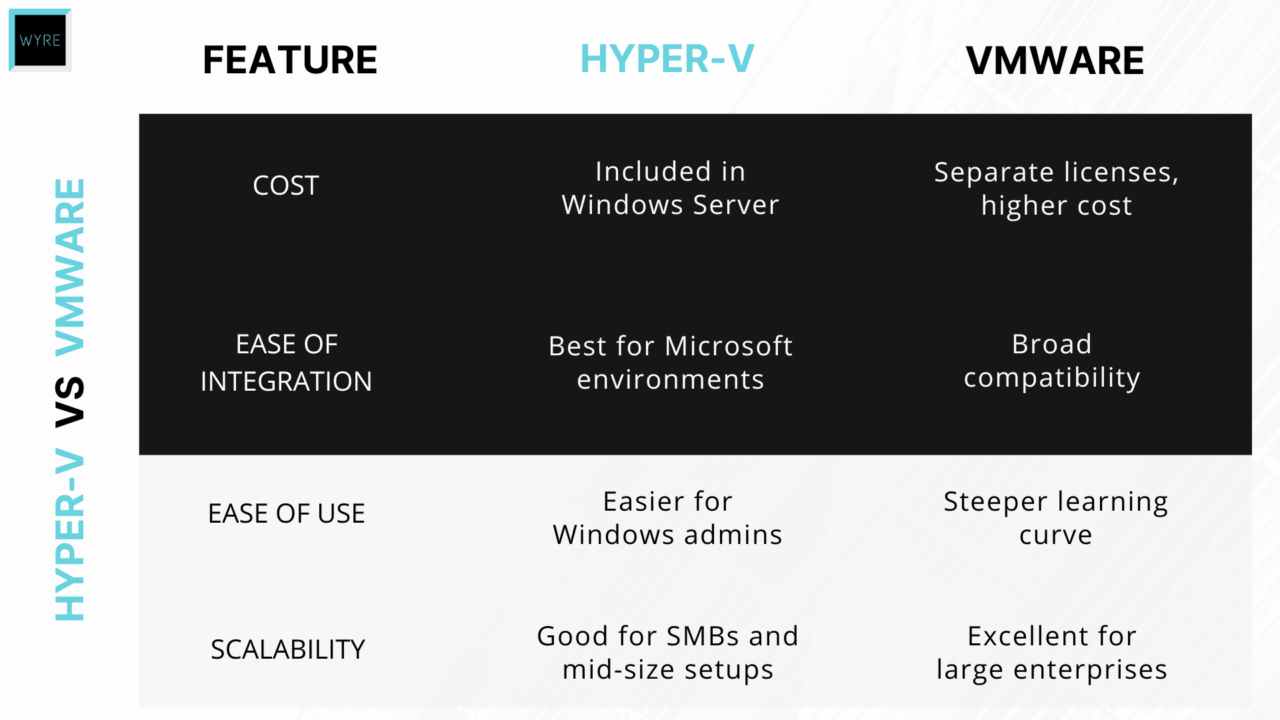
If your business relies on Microsoft, you’ll be glad to know that Hyper-V is included at no additional cost with Windows Server licenses. This makes it a cost-conscious choice for organizations already using Microsoft environments.
You can also purchase it as a standalone product (Hyper-V Server).
Benefits of Hyper-V
- Cost Efficiency: As opposed to Hyper-V being free with Windows Server licenses, VMware requires separate licensing, which can become expensive.
- Seamless Integration with Microsoft Technologies: Hyper-V integrates well with other Microsoft products, including Active Directory, System Center, and Azure. If your business is heavily invested in Microsoft products, this creates a unified environment.
- Ease of Use: Hyper-V’s user-friendly interface and straightforward setup are appealing for businesses with in-house IT teams that are already familiar with Microsoft. VMware is equally powerful, but can have a steeper learning curve for new users.
- Live Migration: Hyper-V supports live migration, allowing VMs to be moved between hosts without downtime. This feature is standard in VMware, as well, but Hyper-V provides it at a lower cost.
- Cost-Effective Disaster Recovery: Hyper-V Replica enables asynchronous replication of VMs to a backup location. This competitive feature compares to VMware's Site Recovery Manager (SRM), but Hyper-V offers it at a lower price point.
Downsides of Hyper-V
- Limited Advanced Features: While Hyper-V covers core virtualization needs, VMware offers more advanced capabilities in areas like storage virtualization (vSAN) and network virtualization (NSX).
- Scalability Constraints: For large enterprise environments, VMware can scale better, offering more comprehensive support for more complex infrastructures.
- Third-Party Tool Integration: VMware has wider compatibility with third-party tools, making it a better choice for IT environments that don't rely solely on Microsoft products.
- Performance: VMware’s ESXi hypervisor often edges out Hyper-V in performance metrics, especially when it comes to high-demand enterprise workloads.
Who Should Choose Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is ideal if your business:
- Operates primarily on Microsoft technologies.
- Has a limited IT budget but requires reliable virtualization.
- Is small to mid-size or new to virtualization.
For enterprises with diverse IT infrastructures, highly complex needs, or the budget for VMware's premium offerings, VMware may still be the better choice.
Nutanix vs. VMware
Nutanix is a leader in hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI). It combines computing, storage, and networking into one system, using software to manage everything. Nutanix’s Acropolis Hypervisor (AHV) is an enterprise-grade hypervisor that offers integrated virtualization solutions.
Benefits of Nutanix
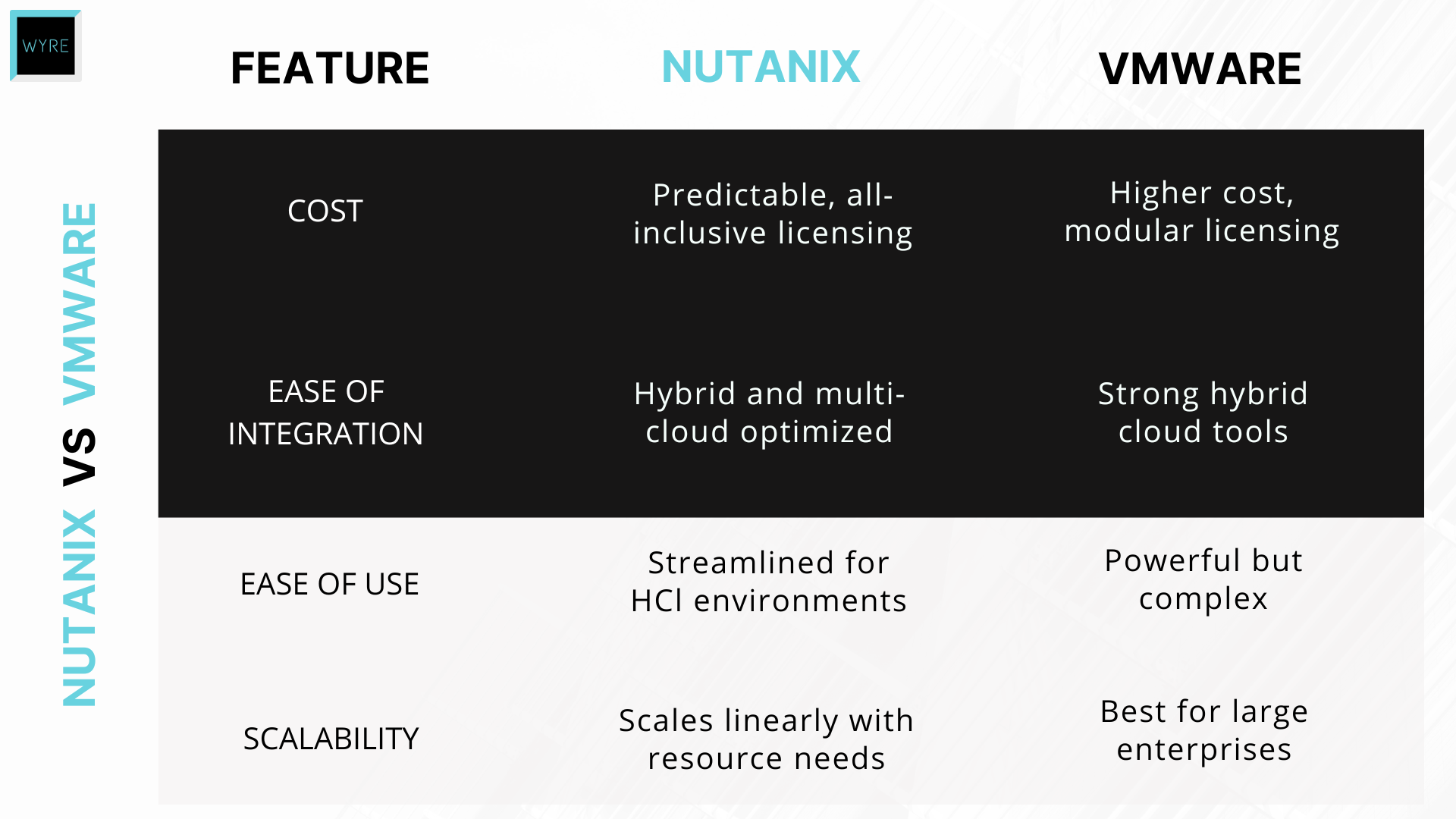
- Hyper-Converged Simplicity: Nutanix eliminates the need for separate storage and computing systems, offering a streamlined solution that’s easier to manage than VMware.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Capabilities: Nutanix is designed with hybrid and multi-cloud environments in mind, allowing businesses to manage workloads both on-prem and in the cloud. VMware offers similar capabilities but often costs more.
- Built-In Automation: Nutanix includes advanced automation tools. This allows your business to simplify operations, including provisioning of VMs and disaster recovery.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: Nutanix makes it easy to add resources as needed without large upfront costs.
- Simplified Licensing Model: Nutanix uses an all-inclusive licensing approach, while VMware’s approach is feature-based.
Downsides of Nutanix
- Learning Curve: IT teams unfamiliar with HCI may need time to adjust to Nutanix.
- Limited Ecosystem: VMware offers more tools and integrations than Nutanix.
- Specialized Focus: Nutanix’s strength lies in HCI and AHV. If you’re looking for traditional virtualization without adopting HCI, VMware is a better fit.
Who Should Choose Nutanix?
Nutanix is an excellent choice if your business:
- Is adopting or transitioning to hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI).
- Needs seamless management of hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Wants a predictable, all-inclusive licensing model.
- Prefers built-in automation tools to keep things simple.
If your organization doesn’t require HCI—or you use a wide variety of third-party tools—VMware may still be the better fit.
Proxmox vs. VMware
Proxmox Virtual Environment (PVE) is an open-source virtualization platform. It uses kernel-based virtual machines (KVMs) to turn a Linux system into a hypervisor. This allows you to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical computer, giving your business budget-friendly versatility.
Benefits of Proxmox
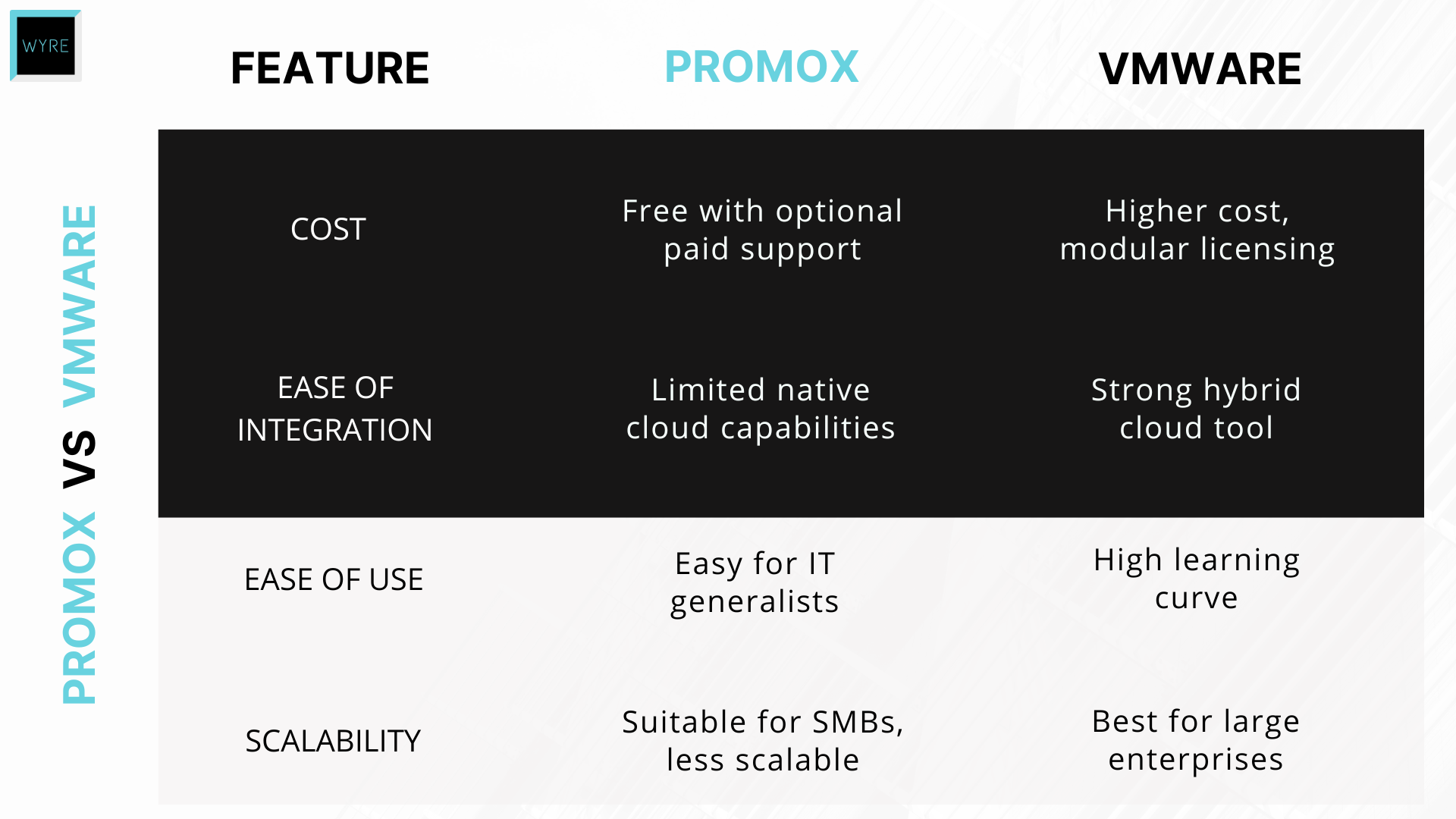
- Cost Savings: Proxmox is open source and free to use, with optional paid support. This makes it a cost-effective alternative to VMware.
- Container Support: In addition to virtual machines, Proxmox natively supports Linux containers (LXC). These offer a less resource-intensive way to package and run applications. Because they exist in isolated environments on a shared operating system, your business gets an efficient alternative to VMs.
- Simplicity and Transparency: The web-based management interface is intuitive, and the open-source nature means you aren’t stuck with one vendor—or hidden fees.
- Active Community Support: Proxmox has a strong, active user community that offers extensive documentation, plugins, and troubleshooting resources.
Downsides of Proxmox
- Enterprise Features: Proxmox lacks some advanced enterprise-grade features available in VMware (e.g., NSX for network virtualization and the same depth of disaster-recovery tools).
- Support for Large Deployments: While suitable for SMBs, Proxmox may not scale as well as VMware in large enterprise environments.
- Smaller Ecosystem: Proxmox's ecosystem of supported tools and integrations is smaller than VMware’s.
Who Should Choose Proxmox
Proxmox is ideal if your business:
- Wants to prioritize cost savings with an open-source virtualization platform.
- Needs container support alongside virtual machines.
- Operates in small- to mid-size IT environments.
- Values simplicity, transparency, and an active community for support.
For large enterprises or businesses needing advanced enterprise-grade features and extensive third-party integrations, VMware remains a better option.
Conclusion
VMware is a powerful, trusted solution for virtualization. But if its recent acquisition leaves you feeling uncertain and keen to explore alternatives, Hyper-V, Nutanix, and Proxmox each offer unique strengths, including seamless Microsoft integration, simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and open-source virtualization.
The right choice depends on your organization's specific needs, priorities, and budget. WYRE can help you evaluate the alternatives, ensuring your business adopts a virtualization platform that aligns with your goals and future growth.
